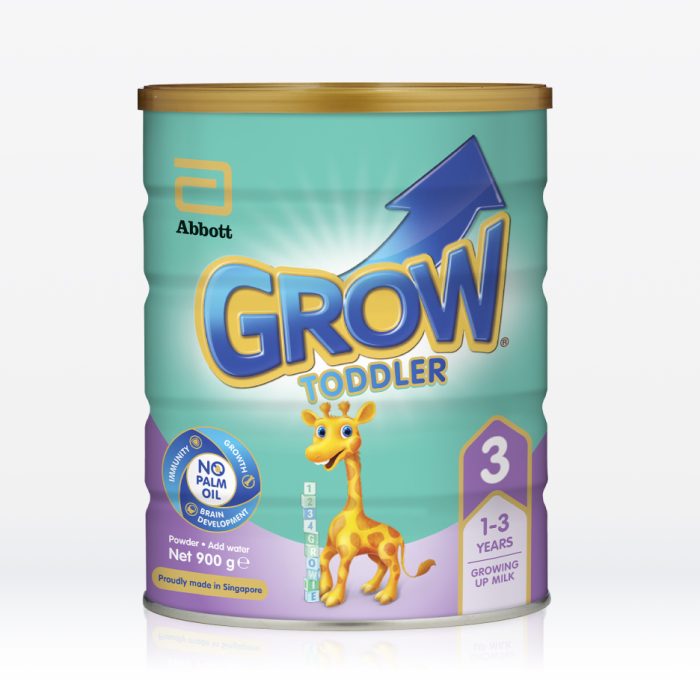
Helps in early childhood growth
What is AA (Arachidonic Acid)?1
Arachidonic acid (AA) is an omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid. It is an integral part of the fat that forms body cell membranes and is abundant in the brain, muscles, and liver. Linoleic acid, a polyunsaturated essential fatty acid that is typically present in plant oils, is used by the body to naturally create AA.
Along with DHA, AA serves as an important building block for the development of the brain and eyes in children.